By: CS2103T T09-B3 Team Since: Sep 2017 Licence: MIT
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Quick Start
- 3. Components
- 4. Key features
- 5. Commands
- 5.1. Viewing help :
(h)help - 5.2. Adding a person :
(a)add - 5.3. Adding an event :
(aE)addE - 5.4. Listing all persons :
(l)list - 5.5. Listing all events :
(lE)listE - 5.6. Editing a person :
(e)edit - 5.7. Editing an event :
(eE)editE - 5.8. Locating persons/events by any property :
(f)find - 5.9. Locating persons by their tag :
(ft)findtag - 5.10. Deleting a person :
(d)delete - 5.11. Deleting an event :
(dE)deleteE - 5.12. Selecting a person:
(s)select - 5.13. Emailing a person :
(em)email - 5.14. Directions to a person’s address :
(gm)gmap - 5.15. Finding a contact on Facebook :
(fb)facebook - 5.16. Adding avatar to a person :
(avr)avatar - 5.17. Switching themes :
(t)theme - 5.18. Listing entered commands :
(his)history - 5.19. Undoing previous command :
(u)undo - 5.20. Redoing the previously undone command :
(r)redo - 5.21. Clearing all entries :
(c)clear - 5.22. Importing data :
(i)import - 5.23. Exporting data :
(p)export - 5.24. Advance setting :
(cfg)config - 5.25. Booking of NUS facilities:
(book)bookNUS - 5.26. Exiting the program :
(x)exit - 5.27. Saving the data
- 5.1. Viewing help :
- 6. FAQ
- 7. Command Summary
1. Introduction
As the name implies, BoNUS helps you better(B) organize(o) your NUS life.
-
As an NUS student, do you feel like your schedules are all over the place and your contacts are too messy making searching through it a pain?
-
Sounds like you need a "Bonus"!
-
Our BoNUS is a desktop personal organizer application dedicated to NUS students to carry out various tasks such as storing contacts, scheduling for upcoming events, timetable planning as well as a calendar to better organise your campus life.
-
Apart from storing essential information such as name, email, address and phone number, you have infinite freedom to customize your own fields!
-
BoNUS is convenient, fast, secured, integrated, solely with the motivation of giving you a bonus for your student life in NUS. It is also oriented for typist users (most operations should be done using keyboard rather than mouse), which makes it all the more simple!
Let’s begin!
1.1. Purpose
This user guide will provide you with a comprehensive step-by-step guide on how to better utilise BoNUS to make your NUS life a breeze.
2. Quick Start
-
Start by ensuring you have Java version
1.8.0_60or later installed in your Computer.Having any Java 8 version is not enough.
If you only have earlier versions of Java 8, this app will not work. -
Download the latest
bonus.jarrelease from here. -
Create a folder you want to use as home folder for BoNUS and copy the
jaryou have downloaded there. -
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI should appear in a few seconds.
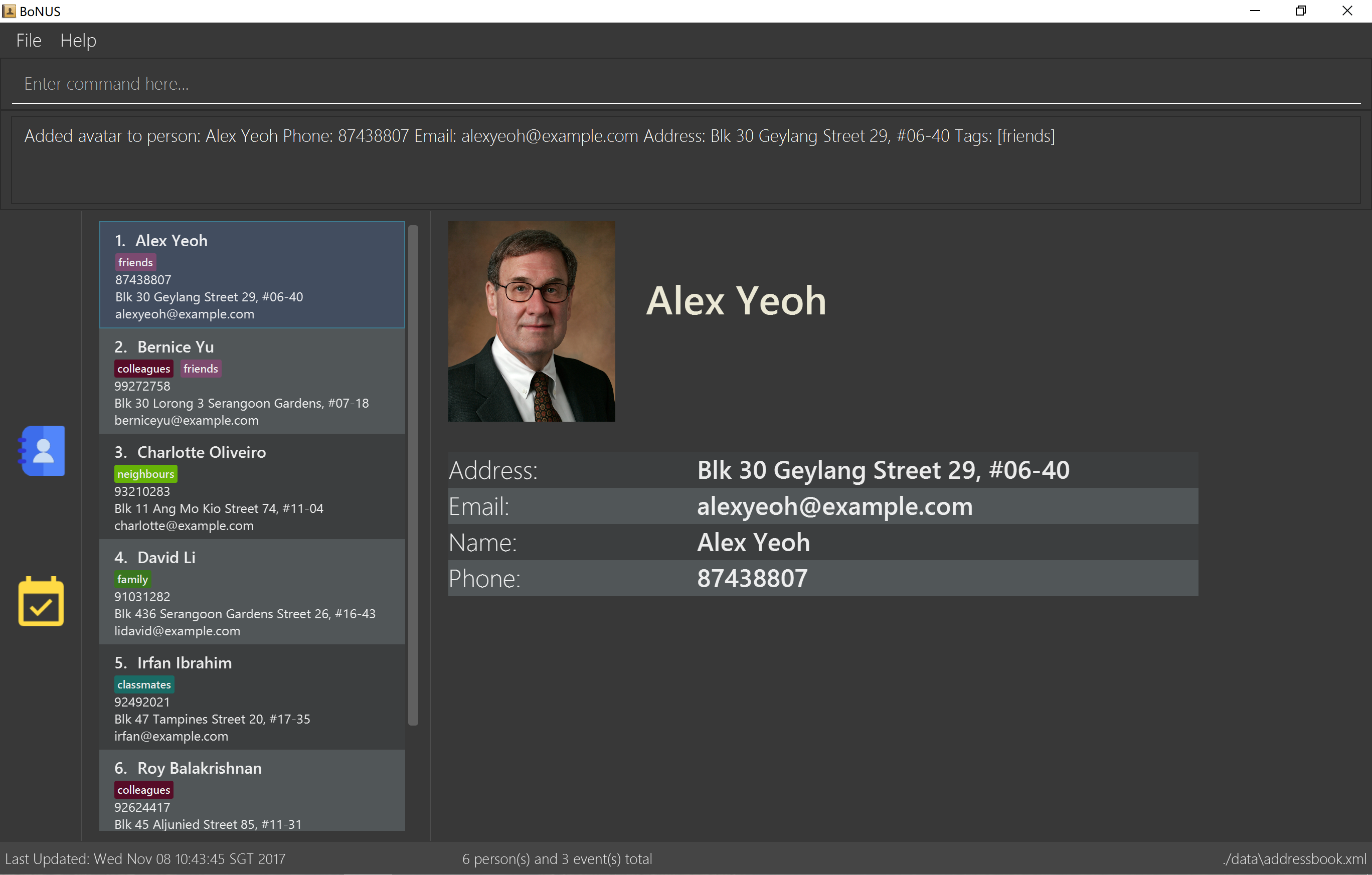
Figure 2.1 : User Interface Demo
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it.
e.g. typinghelpand pressing Enter will open the help window. -
Some example commands you can try:
-
list: lists all contacts -
addn/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01: adds a contact namedJohn Doeto the Address Book. -
delete3: deletes the 3rd contact shown in the current list -
exit: exits the app
-
-
Refer to the commands section below for details of each command.
3. Components
BoNUS consists of three main components: contacts, events and calendar which you can select using the sidebar on the left-hand side.
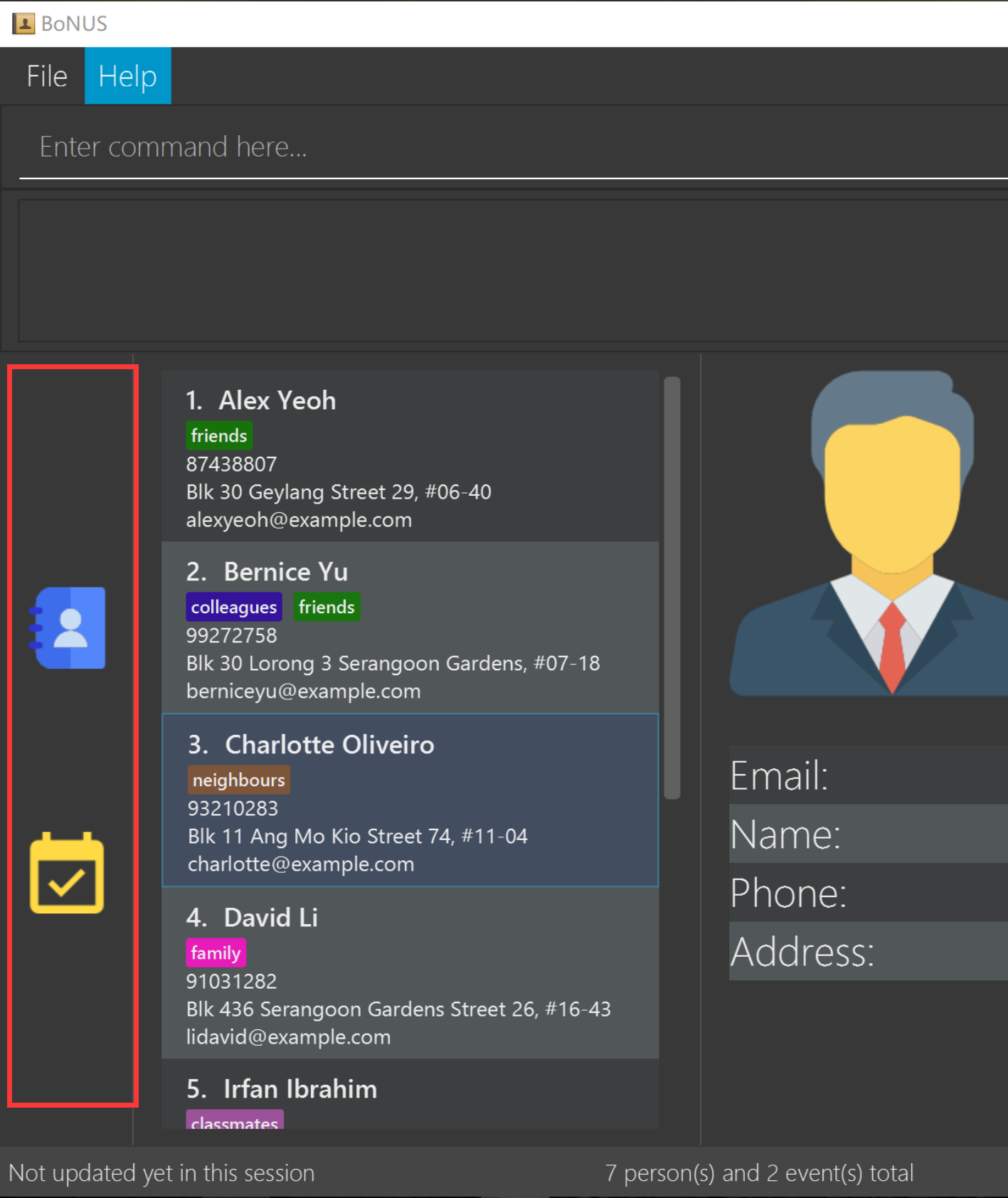
Figure 3.1 : Sidebar for Switching between Different Components
They are described in details as follows:
3.1. Contacts
Time to deal with the many contacts you have accumulated while studying in NUS.
-
By default, you can store and update names, phone numbers, email and mailing addresses. (
addandeditcommand) -
Additionally, you can customize an additional field to a contact that is not in the default. (
config add-propertycommand) -
Now, let’s organize all your contacts by adding one or more tags to them. Those with the same tag will be classified under the same group. You can even customize the colour of the tags to your liking. (
config --set-tag-colorcommand)
3.2. Events
Got a meeting with professor or an assignment deadline you need to remember?
-
By default, you can store and update the title, interval (starting time and end time), venue and description of the event. (
addEandeditEcommand) -
Similar to contacts, you can add customize properties and add tags to events as well.
-
Setting a starting and/or end time for an event, will be reflected accordingly on the calendar component.
-
Reminders will automatically be added upon addition of event and start to notify you from 2 days before the actual event.
-
If one or more of your contacts are attending the event with you, you can link them to the event too.
3.3. Calendar
(Current calendar is static, dynamic calendar coming in v2.0)
Calender provides a clearer image for you to view your upcoming events. All events are displayed based on their time interval for you to be able to attend to them one by one. However, events without time intervals will not be displayed here.
-
You can choose the style to display the upcoming events (weekly/monthly/yearly view).
-
You can add/update/delete events here, but the actual operation will be handled by the events component.
4. Key features
4.1. Convenient
BoNUS is the ultimate application as it will provide you with the utmost convenience and gives you more time to focus on your more important tasks.
-
Import contacts from iCloud, Google+, Facebook, etc.
-
Import events from Google Calendar, Outlook Calendar, etc.
-
Export data (contacts and events) to
.xmlfile (default storage format for BoNUS), Excel Worksheet, etc. -
Sync between all your devices.
-
(Exclusive) automatically generate your school schedule by simply entering your timetable URL from NUSMods.
4.2. Fast
As long as the number of records stored is less than 50,000 and the size of the storage file is smaller than 20MB, BoNUS will be able to
-
Start the application in 5 seconds.
-
Return the result of all commands available with human-invisible delay.
-
Update things displayed on the GUI (graphic user interface) smoothly.
4.3. Secured
The BoNUS developers understand that you will be storing personal data in the application. The following are features of our application that ensures you will have privacy and security.
-
All data saved to the storage file will be encrypted using the state-of-the-art encryption scheme (AES-256).
-
You will be prompted to enter their password whenever they open the application (if you has decided to lock your application the last time before you exited).
-
You can set up 2FA (two-factor authentication) to fulfill extra security requirement(s).
5. Commands
The following is a list of commands that you can use in the application.
Command Format
-
Words in parentheses represent the command shortcut e.g. in
(a)add n/NAME,ais the shorthand-equivalent notation for theaddcommand. -
Words in
UPPER_CASEis information to be supplied by you e.g. inadd n/NAME,NAMEis to be filled in by you. e.gadd n/John Doe. -
Words in square brackets are optional e.g
n/NAME [t/TAG],t/TAGis optional. e.gn/John Doe t/friendor asn/John Doe. -
Items with
… after them can be used from zero times to as many times as you like e.g.[t/TAG]…can be used ast/friend,t/friend t/familyetc. -
You can type the information in any order e.g. if the command specifies
n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER,p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEworks too. -
If parameters with the same prefix are typed multiple times, only the last one will be taken. For example,
n/John Doe n/Martin Henz, then onlyMartin Henzwill be taken into actual consideration.
Command in different components
-
Most commands can be applied to either a person or an event, whose result will depend on the context e.g.
addwill add a person if the user is currently in the contacts component, otherwiseaddEwill add a new event. -
All commands entered in the calendar component will actually be handled by either contacts component or events component.
5.1. Viewing help : (h)help
Have a query? Use the help command!
Format: (h)help (or press F1 on the keyboard)
5.2. Adding a person : (a)add
You just met someone and want to add their contact information into your contact list.
Format: (a)add n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]…
This adds the person to your contact list.
| Your contact can have any number of tags (including 0). |
Examples:
-
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01 -
add n/Betsy Crowe t/friend e/betsycrowe@example.com a/Newgate Prison p/1234567 t/criminal
In a similar format, you can also add customize properties when adding a new person, just use config --add-property
command before to define that property.Notice all pre-defined properties (name, phone, email, address) are compulsory when adding a new person, while customize properties are optional. |
Example:
If you want to add birthday as a field for a contact and use b as the short name,
-
config --add-property s/b f/birthday
Then, you can set a contact’s birthday when you add a new contact (see b/12091191 below)
-
add n/Chris Lee p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/23 Chinatown b/12091991 t/friends
5.3. Adding an event : (aE)addE
You want to record your friend’s birthday party coming up.
Format: (aE)addE n/NAME dt/DATE_TIME a/EMAIL a/ADDRESS
This will add a new event to your list of events.
Examples:
-
addE n/Does Birthday dt/25122015 20:30 a/12 Kent Ridge Drive -
addE n/Betsy Birthday dt/25122016 21:30 a/23 Marina Road
|
|
5.4. Listing all persons : (l)list
You want to view all your contacts in your contact list.
Format: (l)list
This will list out all of your contacts in alphabetical order.
Example:
-
list
| Contacts will be sorted by their names (increment). |
5.5. Listing all events : (lE)listE
Shows a list of all events in the application.
Format: (lE)listE
This will list out all of your events by date/time.
Example:
-
listE
5.6. Editing a person : (e)edit
(Editing of customize properties coming in v2.0)
Edits an existing person in the application.
Format: (e)edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]…
Examples:
-
edit 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.com
Edits the phone number and email address of the 1st person to be91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively. -
edit 2 n/Betsy Crower t/
Edits the name of the 2nd person to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing tags.
5.7. Editing an event : (eE)editE
Edits an existing event in the application.
Format: (eE)editE INDEX [n/NAME] [dt/DATE_TIME] [a/ADDRESS]
Examples:
-
editE 1 dt/18052013 03:30
Edits the date/time the 1st event to be18052013 03:30. -
editE 2 n/Lunch with Betsy
Edits the name of the 2nd event to beLunch with Betsy.
5.8. Locating persons/events by any property : (f)find
(AND and OR search coming in v2.0)
Finds persons/events whose corresponding field(s) contain any of the given keywords.
Format: (f)find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS] [p/KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]]…
Examples:
-
find John
ReturnsjohnandJohn Doe -
find Betsy Tim John
Returns any person having namesBetsy,Tim, orJohn
5.9. Locating persons by their tag : (ft)findtag
Finds persons whose corresponding tags contain any of the given keywords and lists them out.
Format: (ft)findtag KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]…
Examples:
-
findtag family
Returns any person that contains afamilytag -
findtag family colleagues
Returns any person that contains the tagsfamilyandcolleagues
5.10. Deleting a person : (d)delete
Deletes the specified person from the application.
Format: (d)delete INDEX
Examples:
-
list
delete 2
Deletes the 2nd person in the address book. -
find Betsy
delete 1
Deletes the 1st person in the results of thefindcommand.
5.11. Deleting an event : (dE)deleteE
Deletes the specified event from the application.
Format: (dE)deleteE INDEX
Examples:
-
list
deleteE 2
Deletes the 2nd event in the address book.
5.12. Selecting a person: (s)select
Selects a person (identified by the index number used in the last listing) to view the details of that person.
Format: (s)select INDEX
Examples:
-
list
select 2
Selects the 2nd person in the address book. -
find Betsy
select 1
Selects the 1st person in the results of thefindcommand.
5.13. Emailing a person : (em)email
Emails a person (identified by the index number used in the last listing) to email that person.
Format: (em)email INDEX
Examples:
-
list
email 2
Emails the 2nd person in the address book.
5.14. Directions to a person’s address : (gm)gmap
Opens Google Maps in default browser with a person’s (identified by the index number used in the last
listing) address in the Destination.
Format: (gm)gmap INDEX
Examples:
-
list
gmap 2
The address of the 2nd person in the address book will be in the Destination field in Google Maps.
5.15. Finding a contact on Facebook : (fb)facebook
Searches for a person’s (identified by the index number used in the last listing) name on Facebook.
Format: (fb)facebook INDEX
Examples:
-
list
facebook 2
The name of the 2nd person in the address book will be searched on Facebook.
5.16. Adding avatar to a person : (avr)avatar
(Better checking for file type coming in v2.0)
Adds avatar to a person (identified by the index number used in the last listing).
Format: (avr)avatar INDEX IMAGE_PATH
Examples:
-
list
avatar 2 linda.jpg
Adds avatar to the 2nd person in the address book.
|
5.17. Switching themes : (t)theme
Switches between Dark Theme and Bright Theme.
Format: (t)theme
Examples:
-
theme
|
Theme will be saved upon exit. When BoNUS is opened again, theme will be initialized to the theme that was saved previously. |
As shown in Figure 5.15.1 and Figure 5.15.2, Figures depict the Bright Theme and Dark Theme respectively.
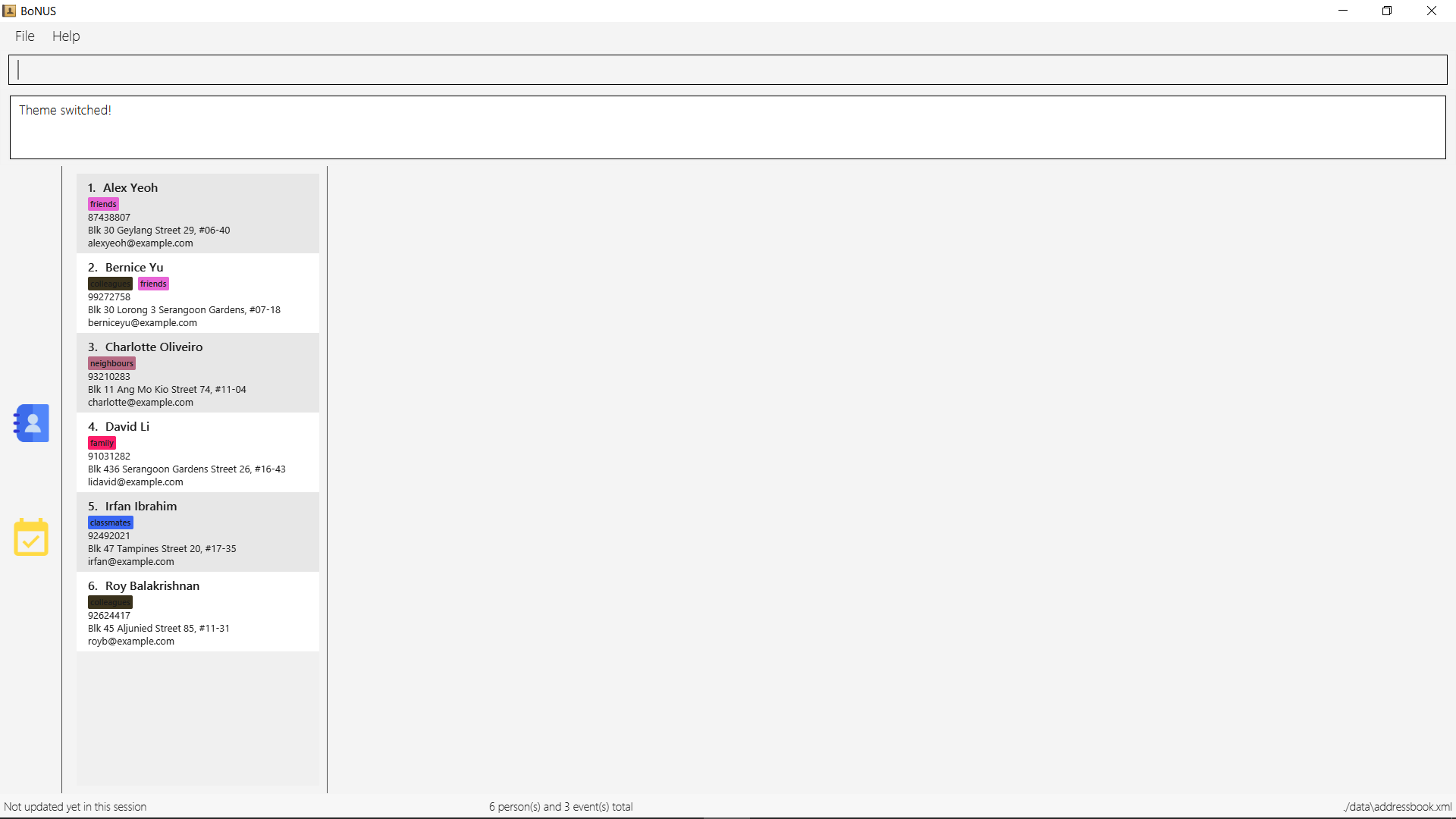
Figure 5.15.1 : Bright Theme
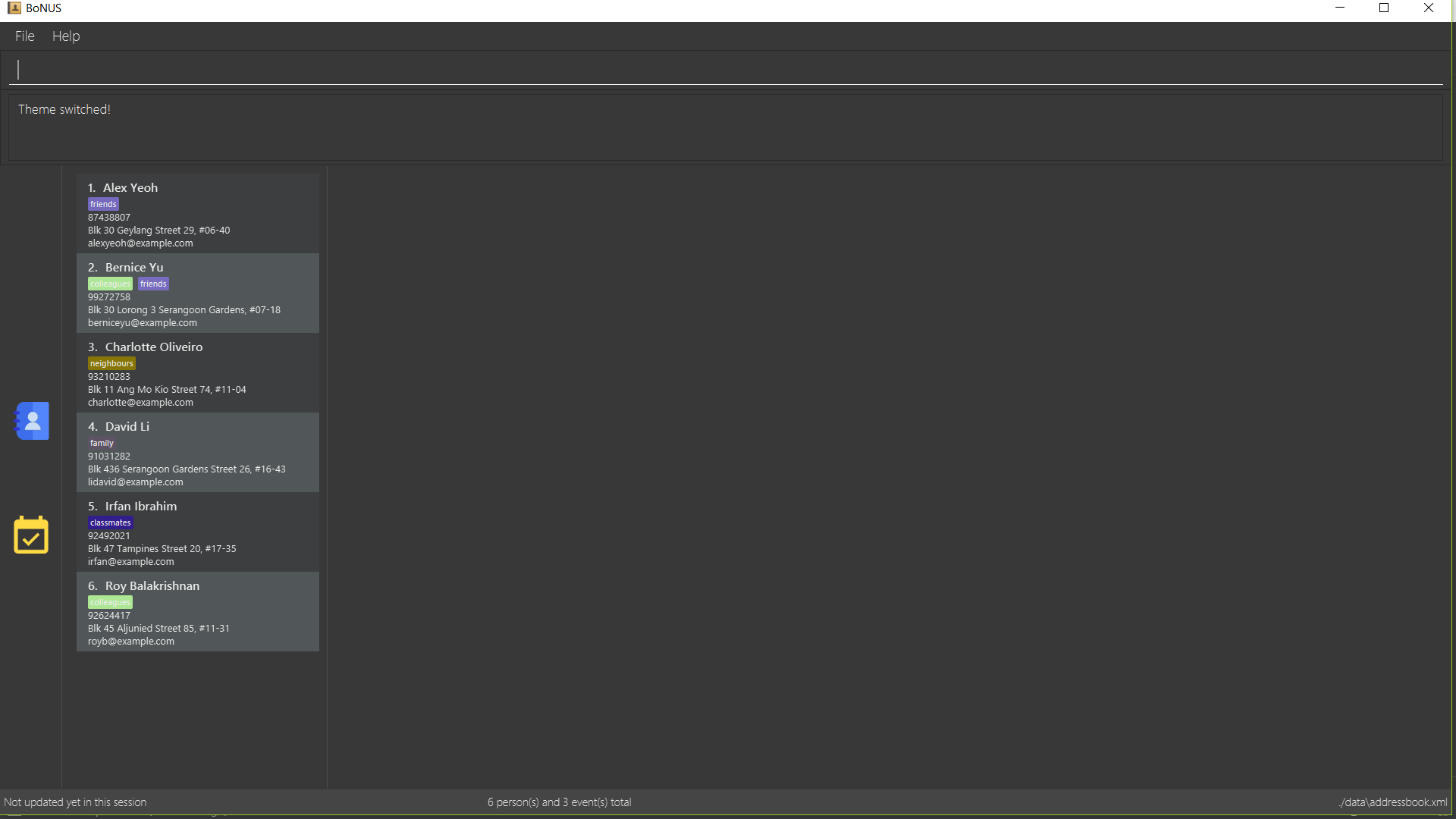
Figure 5.15.2 : Dark Theme
5.18. Listing entered commands : (his)history
Lists all the commands that you have entered in reverse chronological order.
Format: (his)history
Example:
-
history
|
Pressing the ↑ and ↓ arrows will display the previous and next input respectively in the command box. |
5.19. Undoing previous command : (u)undo
Restores the application to the state before the previous undoable command was executed.
Format: (u)undo
|
Undoable commands: those commands that modify the application’s content ( |
Examples:
-
delete 1
list
undo(reverses thedelete 1command) -
select 1
list
undo
Theundocommand fails as there are no undoable commands executed previously. -
delete 1
clear
undo(reverses theclearcommand)
undo(reverses thedelete 1command)
| You can view what command you have undone from the user feedback message. |
5.20. Redoing the previously undone command : (r)redo
Reverses the most recent undo command.
Format: (r)redo
Examples:
-
delete 1
undo(reverses thedelete 1command)
redo(reapplies thedelete 1command) -
delete 1
redo
Theredocommand fails as there are noundocommands executed previously. -
delete 1
clear
undo(reverses theclearcommand)
undo(reverses thedelete 1command)
redo(reapplies thedelete 1command)
redo(reapplies theclearcommand)
| You can view what command you have redone from the user feedback message. |
5.21. Clearing all entries : (c)clear
Clears all entries from all components (both contacts and events).
Format: (c)clear
Example:
-
clear
5.22. Importing data : (i)import
5.22.1. From .xml format
Imports the data in an external XML file, including data from all three components: Contacts, Events and Calendar,
into the current address book of BoNUS.
Format: (i)import FILEPATH
|
The default data format is |
Examples:
-
For
Windowsusers:
import C:\Users\John Doe\Documents\bonus.xml -
For
macOSandLinuxusers:
import /Users/John Doe/Documents/bonus.xml
|
For |
5.22.2. From .bo format
(Coming in v2.0)
Imports the data in an external BoNUS script file (which ends with .bo), including data from all three components:
Contacts, Events and Calendar, into the application.
Format: (i)import --script FILEPATH
Examples:
-
For
Windowsusers:
import --script C:\Users\John Doe\Documents\bonus.bo -
For
macOSandLinuxusers:
import --script /Users/John Doe/Documents/bonus.bo
|
For |
5.22.3. From NUSMods URL
(Exclusive feature for NUS students)
The BoNUS team understands that NUSMods has become an indispensable school timetable builder
for almost all students at NUS. Thus, you are definitely allowed to import your timetable from NUSMods to the BoNUS
application.
Format: (i)import --nusmods YOUR_NUSMODS_URL
Example:
-
import --nusmods https://nusmods.com/timetable/2017-2018/sem1?CS2103T[TUT]=C01
|
5.22.4. From Google Accounts
(Coming in v2.0)
Imports your contacts and events from Google Contacts and Google Calender respectively.
Format: (i)import --google https://myaccount.google.com/
Example:
import --google https://myaccount.google.com/
|
5.23. Exporting data : (p)export
5.23.1. To .xml format
Exports the current data in the application, including data from all three components: Contacts, Events and
Calendar, to an external location.
Format: (p)export FILEPATH
Examples:
-
For
Windowsusers:
export C:\Users\John Doe\Documents\bonus.xml -
For
macOSandLinuxusers:
export /Users/John Doe/Documents/bonus.xml
|
For |
5.23.2. To Microsoft ExcelTM Worksheet
(Coming in v2.0)
Exports the current data in the application to an external file of Microsoft ExcelTM format.
Format: (p)export --excel FILEPATH
Examples:
-
For
Windowsusers:
export --excel C:\Users\John Doe\Documents\bonus.xls -
For
macOSandLinuxusers:
export --excel /Users/John Doe/Documents/bonus.xls
|
For |
5.24. Advance setting : (cfg)config
Changes the configuration of the application or applies some advance settings to the data. Make sure you know what you are doing before using any of the following commands. These commands are intended for advance users.
5.24.1. Adding a customize property : (cfg)config --add-property
Adds a new customize property field available to all persons or events.
Format: (cfg)config --add-property s/SHORT_NAME f/FULL_NAME [m/MESSAGE r/REGULAR_EXPRESSION]
Example:
-
config --add-property s/ag f/age -
config --add-property s/b f/birthday m/Birthday should be in the format of DD/MM/YYYY r/[^\s].*
|
5.24.2. Setting the tag color : (cfg)config --set-tag-color
(Tag feature for events coming in v2.0)
Sets the displayed color of a certain tag (for persons/events).
Format: (cfg)config --set-tag-color TAG_NAME COLOR
Example:
-
config --set-tag-color friends red
|
If you enter an invalid color name, the background for that tag will be set to transparent temporarily. You can use this again to set it to a legal color. |
5.25. Booking of NUS facilities: (book)bookNUS
(Exclusive feature for NUS students)
(Coming in v2.0)
The BoNUS team understands that booking of facilities in NUS may be troublesome. Therefore, we have decided to integrate the facility booking website with BoNUS such that upon successful booking of a specific facility, your Events List will be updated accordingly with the Date, Time and Venue of booking.
Format: (book)bookNUS
-
Upon execution the command, you will be brought the the NUS facility booking website on a separate browser.
-
Upon successful booking of the facility, Event with date, time and venue will automatically be added as events to the application.
Example:
-
bookNUS
|
5.27. Saving the data
-
Address book data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data.
-
These commands are also called undoable commands.
-
There is no need to save manually.
6. FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the
data of your previous Address Book folder.
7. Command Summary
-
Add :
(a)add n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]…
e.g.add n/James Ho p/22224444 e/jamesho@example.com a/123, Clementi Rd, 1234665 t/friend t/colleague -
Add event :
(aE)addE n/NAME dt/DATE_TIME a/ADDRESS
e.g.addE n/James birthday dt/18022017 13:30 a/123, Clementi Rd, 1234665 -
Clear :
(c)clear -
Delete :
(d)delete INDEX
e.g.delete 3 -
Delete event :
(dE)deleteE INDEX
e.g.deleteE 3 -
Edit :
(e)edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE_NUMBER] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]…
e.g.edit 2 n/James Lee e/jameslee@example.com -
Edit event :
(eE)editE INDEX [n/NAME] [dt/DATE_TIME] [a/ADDRESS]
e.g.editE 2 n/Lees Day -
Find :
(f)find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
e.g.find James Jake -
List :
(l)list -
List event :
(lE)listE -
Switch Themes :
(t)theme -
Help :
(h)help -
Select :
(s)select INDEX
e.g.select 2 -
History :
(i)history -
Undo :
(u)undo -
Redo :
(r)redo -
Exit :
(x)exit -
Import :
(i) From.xmlfile:import FILEPATH
eg. ForWindowsusers:import C:\Users\John Doe\Documents\bonus.xml
eg. FormacOSandLinuxusers:import /Users/John Doe/Documents/bonus.xml
(ii) From script file:import --script FILEPATH
eg. ForWindowsusers:import C:\Users\John Doe\Documents\bonus.bo
eg. FormacOSandLinuxusers:import /Users/John Doe/Documents/bonus.bo
(iii) From NUSMods timetable:import --nusmods URL
eg.import --nusmods https://nusmods.com/timetable/2017-2018/sem1?CS2103T[TUT]=C01 -
Export :
(p)export [--excel] FILEPATH
eg. ForWindowsusers:export C:\Users\John Doe\Documents\bonus.xml
eg. FormacOSandLinuxusers:export /Users/John Doe/Documents/bonus.xml -
Config :
(i) Add customize property(cfg)config --add-property
eg.config --add-property s/b f/birthday
(ii) Change tag color(cfg)config --set-tag-color
eg.config --set-tag-color friends blue